In the twilight of 1998, the iconic Lockheed SR-71 Blackbird took its final bow, concluding an illustrious 30-year chapter in the annals of the United States Air Force. With a legacy etched in the skies, the Blackbird soared above and beyond, shattering records throughout its three-decade reign. Now, emerging from the shadows of secrecy, Lockheed Martin unveils its ambitious successor – the SR-72, aptly dubbed the “Son of Blackbird,” poised to carry forward the legacy of its legendary predecessor and, perhaps, etch its own indelible mark in the stratosphere of aviation history.

Announced in 2013, the revelation of the proposed hypersonic aircraft sent shockwaves through the aerospace community. This cutting-edge marvel, the SR-72, holds the promise of transcending the boundaries of contemporary aviation. Envisioned to redefine the skies, this hypersonic successor to the legendary Blackbird could potentially make its debut in operational service as early as 2030, provided that the intricate threads of planning and development seamlessly weave together. The unfolding narrative of the SR-72 beckons, as it stands at the precipice of revolutionizing air travel and pushing the limits of what was once deemed impossible.
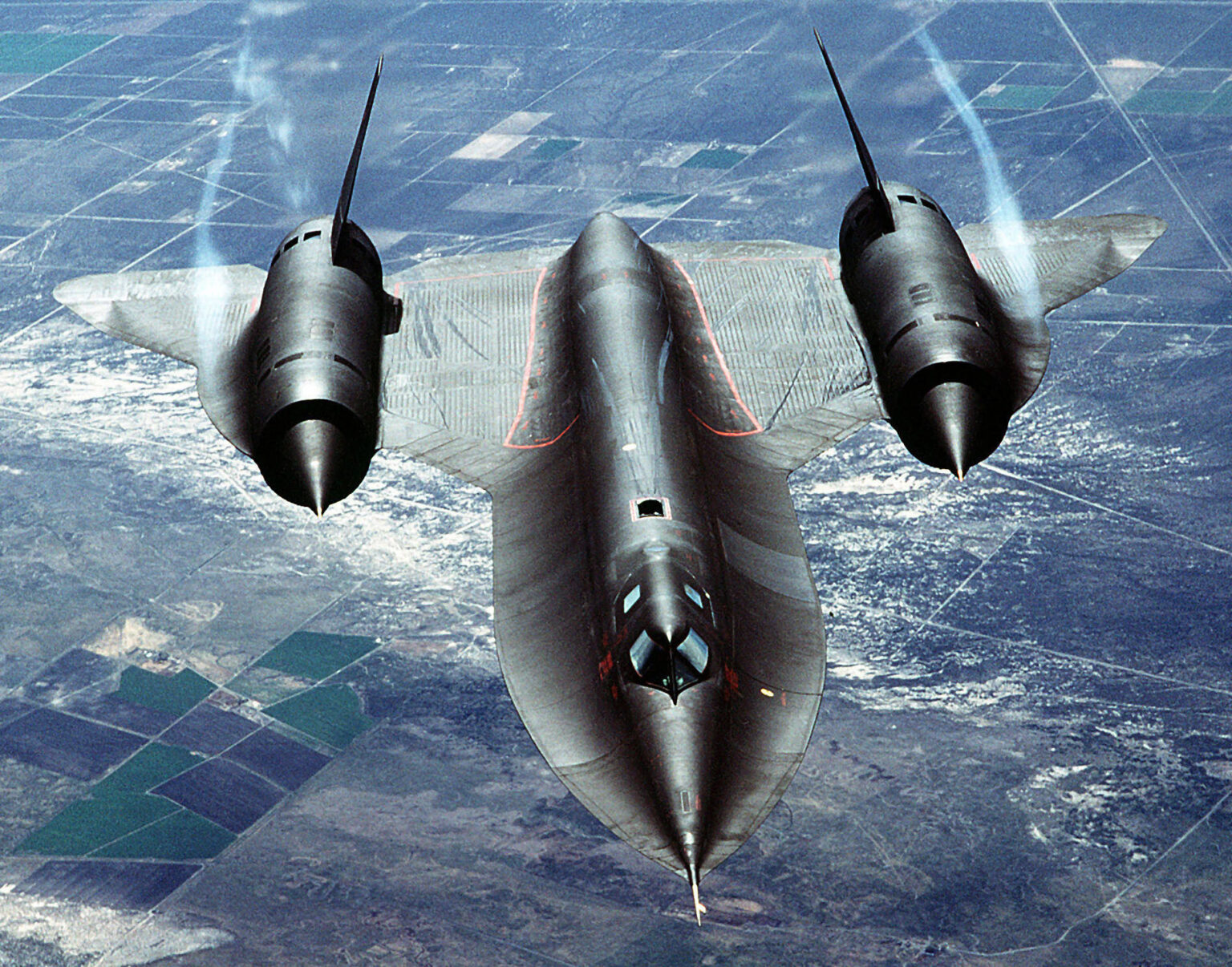

The Lockheed SR-71 Blackbird, a marvel of long-range, high-altitude strategic reconnaissance, made its indelible mark on the skies when it entered service with the US Air Force in 1966. A direct successor to the short-lived Lockheed A-12, the SR-71 was meticulously designed with an emphasis on increased size for enhanced fuel capacity and improved speed, a testament to human ingenuity reaching new heights.
Crafted from titanium sourced even from the Soviet Union, this technological masterpiece was built to withstand the punishing speeds exceeding Mach 3, ensuring it soared through the skies unscathed. Its operational debut, however, was not without challenges, notably the loss of components after each mission. To mitigate this, each unit underwent flight only once a week, minimizing downtime for recovery.
Stationed primarily in Okinawa, Japan, with missions spanning Europe and active involvement in conflicts like the Yom Kippur War, the SR-71 demonstrated its strategic importance. Despite the hurdles, the aircraft served with distinction until its retirement by the Air Force in 1998, leaving an enduring legacy. Remarkably, NASA continued to operate the SR-71 for an additional year after the official Air Force retirement. The aircraft’s final curtain call occurred on October 9, 1999, marking the end of an era as the remaining units found their resting place in museums, immortalized for generations to come.

The retirement of the legendary SR-71 Blackbird left a conspicuous void in the US Air Force’s arsenal, prompting the need for a high-speed successor capable of penetrating protected airspace to observe targets or execute strategic strikes before the enemy could react.
Rumblings about Lockheed Martin’s development of such an aircraft, rumored to achieve speeds exceeding Mach 6, first surfaced in 2007. However, it wasn’t until 2013, through an article in Aviation Week & Space Technology, that the existence of this advanced aircraft was officially confirmed. Since then, the project’s progress and development have been shrouded in occasional discussions, with scant concrete information publicly disclosed.
The SR-72 stands as a beacon of innovation, a testament to Lockheed Martin’s commitment to pushing the boundaries of aeronautical engineering. As the aircraft continues to emerge from the shadows of secrecy, the poster serves as a captivating glimpse into the future of air dominance, paying homage to the legacy of the Blackbird while heralding the dawn of a new era in aerial prowess.
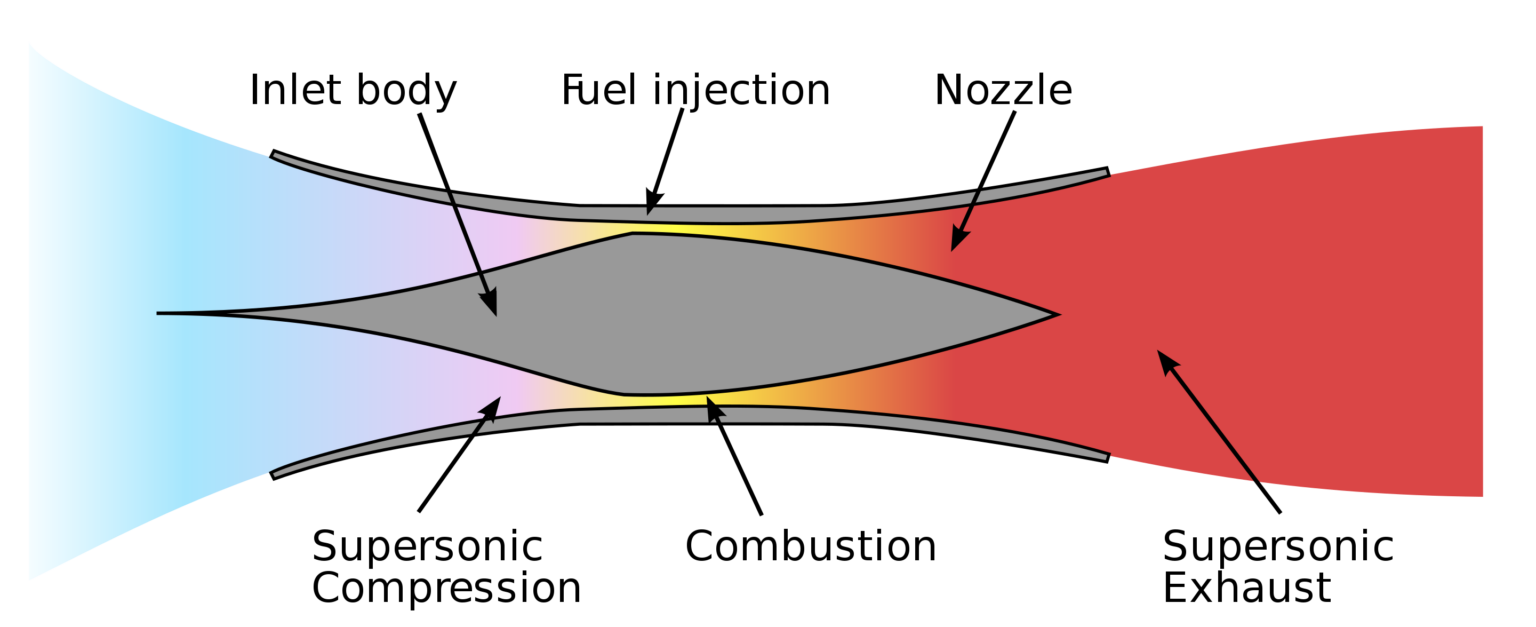
In pursuit of the SR-72’s ambitious speed goals, Lockheed Martin finds itself at the forefront of innovation, navigating the challenges of developing an engine capable of operating under extreme temperatures. Collaborating with Aerojet Rocketdyne, the aerospace giant is embarking on a groundbreaking venture to resurrect the concept of the canceled scramjet-powered HTV-3X, now reincarnated as a “turbine-based combined cycle” (TBCC) system. This innovative approach involves the utilization of a turbine engine at lower speeds, seamlessly transitioning to a scramjet engine at higher velocities.
Recognizing the monumental task at hand, NASA has thrown its weight behind Lockheed Martin’s engine development efforts, awarding the company a substantial $892,292 contract. This financial endorsement underscores the significance of the SR-72 project and propels the collaboration toward overcoming the engineering challenges that lie ahead.
Beyond the engine, the SR-72 demands an outer coating that can withstand the harsh conditions at its proposed altitude of 80,000 feet, where exceeding Mach 5 poses the risk of melting typical metallic airframes. Enterprising solutions are being explored, with a melding of ceramic, high-performance carbon, and metal materials emerging as potential candidates. This strategic amalgamation aims to create an outer shell robust enough to endure the searing heat generated at hypersonic speeds, pushing the boundaries of aeronautical engineering to new frontiers.
As Lockheed Martin ventures into uncharted territory with the SR-72, the collaboration with NASA and the innovative TBCC system signify not just the evolution of aircraft design but a profound leap into the future of aerospace technology.
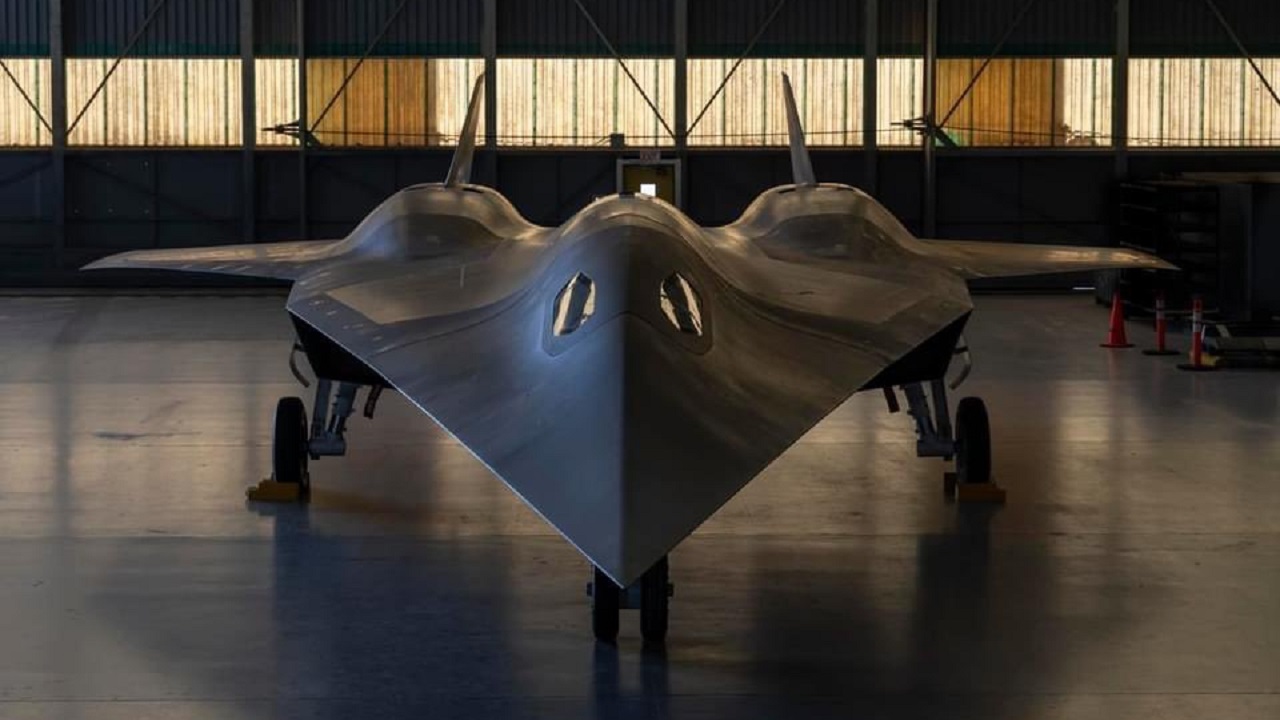

On a positive note, the SR-72’s unmanned nature alleviates concerns about human occupants, emphasizing its role as an unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV). This autonomy enhances its potential applications in strategic scenarios without risking human lives.
As the SR-72 evolves into a formidable platform, the nature of its payload becomes a critical consideration. Envisioned as a versatile strike and Intelligence, Surveillance, and Reconnaissance (ISR) platform, its primary objective is to observe targets while retaining the capability to execute precise attacks. This ambitious mission profile necessitates the development of new weapons and sensors, with emerging reports indicating the likely integration of Lockheed Martin’s High-Speed Strike Weapon (HSSW).
Beyond these specifics, the SR-72’s enigmatic veil shrouds certain details. However, it is known that the aircraft will approximate the size of its legendary predecessor, the SR-71 Blackbird, exhibiting a sleek and aerodynamic design that echoes the cutting-edge ethos of Lockheed Martin’s engineering prowess.
The lingering question remains: When will the Lockheed Martin SR-72, the ‘Son of Blackbird,’ take to the skies in active service? The answer to this inquiry is a tantalizing prospect that awaits, echoing the anticipation that surrounds the emergence of this next-generation hypersonic marvel.
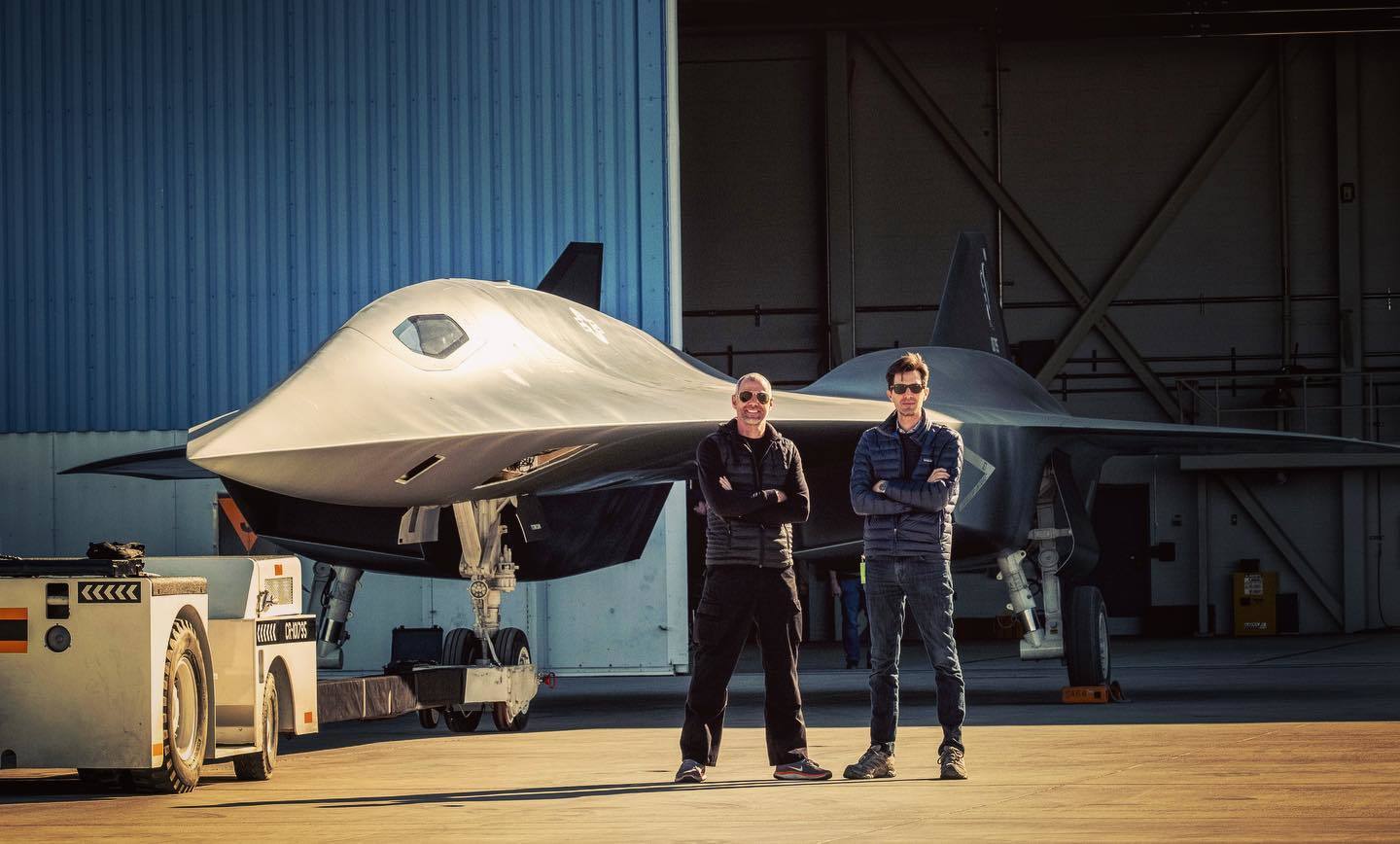
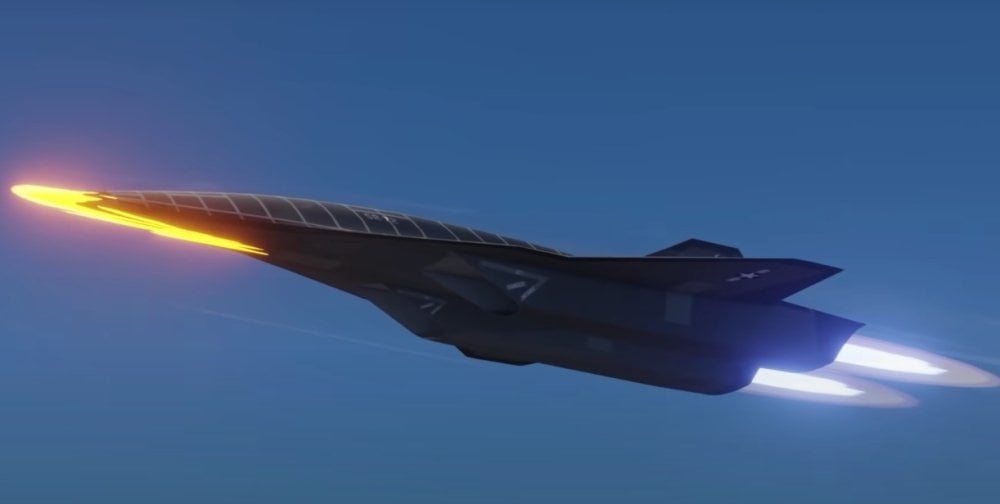


At present, the gears of innovation are turning to construct not the SR-72 itself but rather a demonstrator, a tangible testament to Lockheed Martin’s vision. This precursor will serve as a critical proving ground, showcasing the technological prowess and feasibility of the ambitious SR-72 project. The fate of this endeavor hinges on the green light that Lockheed Martin eagerly awaits, signaling the authorization to propel the project into full-scale development.
The SR-72 has recently captured public imagination with a cinematic nod in the 2022 blockbuster, “Top Gun: Maverick.” In this cinematic saga, Tom Cruise reprises his iconic role as Pete “Maverick” Mitchell, and the spotlight is turned on an aircraft known as the SR-72 Darkstar. Remarkably, this fictional aircraft is said to draw inspiration from Lockheed Martin’s real-world project, injecting a dose of intrigue and anticipation into the narrative surrounding the SR-72. As the world watches the skies in both reel and reality, the SR-72 emerges as a symbol of the convergence between cinematic imagination and the cutting-edge innovations shaping the future of aviation.